High-quality Precision Grinding Services in Days Not Weeks | Free Standard Shipping on All US Orders | Subject to availability. Xometry doesn’t guarantee that we can provide this service at any given time.
All uploads are secure and confidential.
Xometry’s Instant Quoting Engine is covered by U.S. Pat. Nos. 11,086,292, 11,347,201, 11,693,388, 11,698,623, 12,099,341, and 12,189,361. Other patents pending.
Precision grinding, like all grinding processes, employs an abrasive material to remove small pieces of material from a workpiece. Precision grinding is focused on producing very flat, smooth surfaces, working to very tight tolerances.
Xometry’s high-quality precision grinding services have attracted customers in a wide range of industries including: automotive, aviation, bearing, electrical, and medical. Xometry offers four different types of precision grinding services: cylindrical grinding, centerless grinding, internal grinding, and spindle grinding.
Precision grinding is a finishing process used in manufacturing to remove small amounts of material from a workpiece. An abrasive grinding tool, usually a rotating wheel or belt, contacts the workpiece and facilitates material removal. Grinding is typically used as a finishing process and is a cost-effective and reliable way to obtain precise tolerances and beautiful surface finishes on a manufactured part. Precision grinding is often used to satisfy highly precise tolerances as low as +0.00025”. Additionally, the process is often used to obtain polished surface finishes on parts. Precision grinding can be used as a final finishing process or can be used to prepare parts for other finishing processes like honing, lapping, and superfinishing.
Precise dimensions and desirable surface finishes are made possible in precision grinding processes by the use of abrasives such as: aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, and diamond. The type of abrasive used depends on the workpiece material. For example, aluminum oxide abrasives are best for grinding steel and other ferrous metals, while silicon carbide abrasives are better for non-ferrous metals. While grinding can be completed manually using equipment like belt grinders and angle grinders, CNC automated grinding produces superior results in terms of efficiency and surface quality.
Xometry offers four main types of precision grinding used in various industries including automotive, aerospace, and machinery. The four processes are described below:
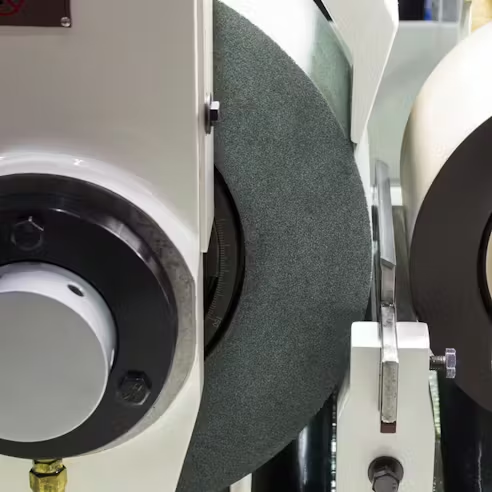
Cylindrical grinding is a machining process in which the cylindrical workpiece and the grinding tool rotate simultaneously. Cylindrical grinding is ideal for grinding the external surfaces of rotationally symmetric workpieces to achieve extremely accurate dimensions. Additionally, the process can replace lathe operations. It is used to remove material from exceptionally hard workpieces. In cylindrical grinding, the workpiece is mounted on the centers of its two opposite, perpendicular faces. While the workpiece rotates, an abrasive grinding wheel rotates in the opposite direction and removes material.
In the centerless grinding process, a cylindrical workpiece rests on a support between a grinding wheel and a regulating wheel. In this process, the grinding wheel and regulating wheel rotate in the same direction. The larger grinding wheel pushes the workpiece against both the regulating wheel and the support, and the regulating wheel dictates the workpiece’s rotational speed. As the grinding wheel, regulating wheel, and workpiece rotate, the material is removed and precise dimensions can be attained. Round parts are not required to be gripped in a chuck or fixture and are not ground between centers. Centerless grinding, compared to cylindrical grinding, enables higher throughput since parts do not need to be fixed in a machine’s jaws.
Internal grinding is similar to cylindrical grinding in that the workpiece is fixed and ground between its centers. However, it differs from cylindrical grinding since only one side is fixed in the machine’s jaws. Internal grinding uses separate motors for rotating the grinding tool and for rotating the workpiece. Like in cylindrical grinding, the grinding wheel and workpiece are in opposite directions. The grinding wheel is fed in and out of the part to achieve precise dimensions on internal holes.
Spindle grinding is a type of grinding that uses a grinding wheel oriented either perpendicular (vertical spindle grinding) or parallel (horizontal spindle grinding) to the table. This type of grinding is best for flat parts. A rotating grinding wheel removes material from flat and angled surfaces, tapers, and slots in vertical spindle grinding. In horizontal spindle grinding, the workpiece is placed on a reciprocating table or a rotary table and fed into a stationary, rotating grinding wheel.
Precision grinding benefits are listed and described below:

Precision grinding is a cost-effective process because of its ability to achieve precise dimensions in large volumes of parts. Not only is the process fast, but it’s also versatile and highly reliable. Precision grinding can be used on a wide array of materials, including hardened steel and non-ferrous metals, and seldom produces non-conforming parts.
A high degree of accuracy is a huge advantage of precision grinding. In manufacturing, machining processes like milling and turning are used to achieve dimensions close to what is required. While required dimensions can often be achieved with these machining processes, grinding enables manufacturers to remove tiny amounts of material to create extremely accurate parts.
Precision grinding is a highly reliable process. Defects seldom occur during grinding processes, since the process is easy to set up, highly efficient, and applies less pressure to the workpiece than other processes used to obtain precise dimensions like machining.
Tight tolerances are another advantage of precision grinding. With precision grinding, Xometry can achieve tolerances as tight as +0.00025”. Tolerances this low are great for parts commonly manufactured for the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries. Especially in the medical industry where parts are fitted to or implanted into a person’s body, precise parts are absolutely essential.
Precision grinding produces very smooth surface finishes. This is important not just for functionality, such as in medical parts like surgical instruments, but also for the aesthetic qualities of the finished product.
Precision grinding is not without its disadvantages. Some disadvantages of the process are listed below:

Precision grinding takes time, which makes it expensive. Fabricators and customers should agree on whether this process is really necessary, or whether the tolerances achieved by milling or turning will be sufficient for the application.
Precision grinding machines require a high initial investment. Making the business case for this type of capital expenditure requires a close study of the current business cash flow and the projections for increased business due to the increased process capability offered by having a precision grinding machine in-house.
For parts that require high purity such as in the medical, semiconductor, and food service industries, precision grinding could leave behind debris from either the grinding wheel abrasive or the small particles removed from the part surface. Such contaminants can compromise the function or cleanliness of the part.
Several industries use precision grinding to achieve parts with tight tolerances and aesthetically pleasing surfaces. Whether joining parts in an automotive assembly or ensuring that surface finish requirements for surgical instruments are met, precision grinding allows manufacturers to reliably produce precise parts. Some industries where precision grinding is commonly used are listed below.
Precision grinding methods like cylindrical grinding and spindle grinding are often used in the automotive industry to achieve low tolerances in parts that go into assemblies such as bearings in gearboxes and wheels, crankshafts, gears, and axles.
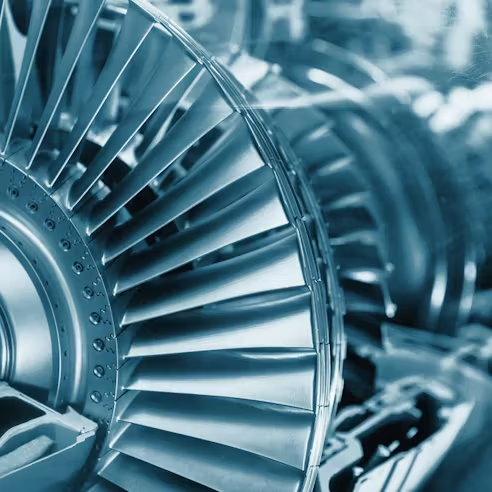
Cylindrical grinding, centerless grinding, and creep feed grinding are three precision grinding methods commonly used in the aerospace industry. These methods are often used to obtain precise dimensions in bearings, landing gear components, engine components, and turbine components like blades, shrouds, and vanes.
Precision grinding methods like internal grinding and cylindrical grinding are often used to achieve tight tolerances in bearings. Extreme precision is required for bearings to ensure the proper fit and function of the assemblies bearings are used in. Bearings support both linear and rotary motion, depending on the application. Different applications that use bearings include: motors, pumps, gearbox and wheel bearings in cars, skateboard wheels, jewelry and watches, and more.
Grinding processes like spindle grinding and cylindrical grinding are commonly used in the electrical industry for components in electrical motors and electronics, semiconductors, heat sinks, and more. Many electrical components require precise dimensions to fit in compact assemblies and enclosures. Additionally, many components require surfaces to be smooth to help them function as intended.
Precision grinding is commonly used in the medical industry for parts like surgical and dental instruments, prosthetic components, and implants. Precision and high quality are essential to ensuring the best patient outcomes and patient safety since many of these parts are used in human bodies
For some parts, abrasive grinding may not be ideal. Xometry offers several alternatives to precision grinding. Those options are listed and described below:


Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.

Get started with our easy-to-use platform and let our experts take care of managing the project from locating the right manufacturing partner to delivery logistics.

We are ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, and AS9100D certified. Only the top shops that apply to become suppliers make it through our qualification process.
All uploads are secure and confidential
