Metals Alloy Guidance, Manufacturing Considerations & Finishing
Comprehensive reference for selecting metals across machined parts, castings, forgings, extrusions and stamped components. Includes common alloys, key properties, DFM tips, processing notes and finishing compatibility to help you choose the right metal for performance and manufacturability.
- Aluminum, stainless & carbon steels, zinc alloys, copper/brass and titanium
- Manufacturing notes for machining, casting, forging, stamping and welding
- Finishing compatibility, corrosion considerations and MTR/testing guidance
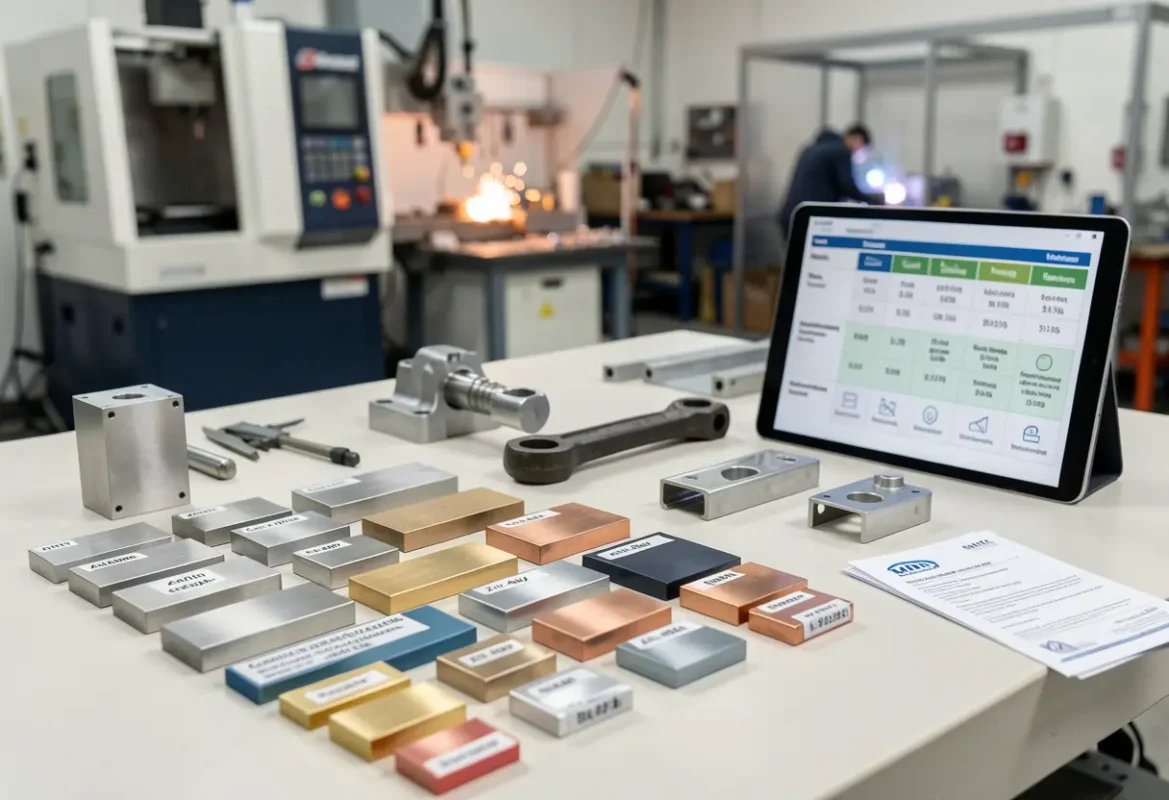

Capabilities
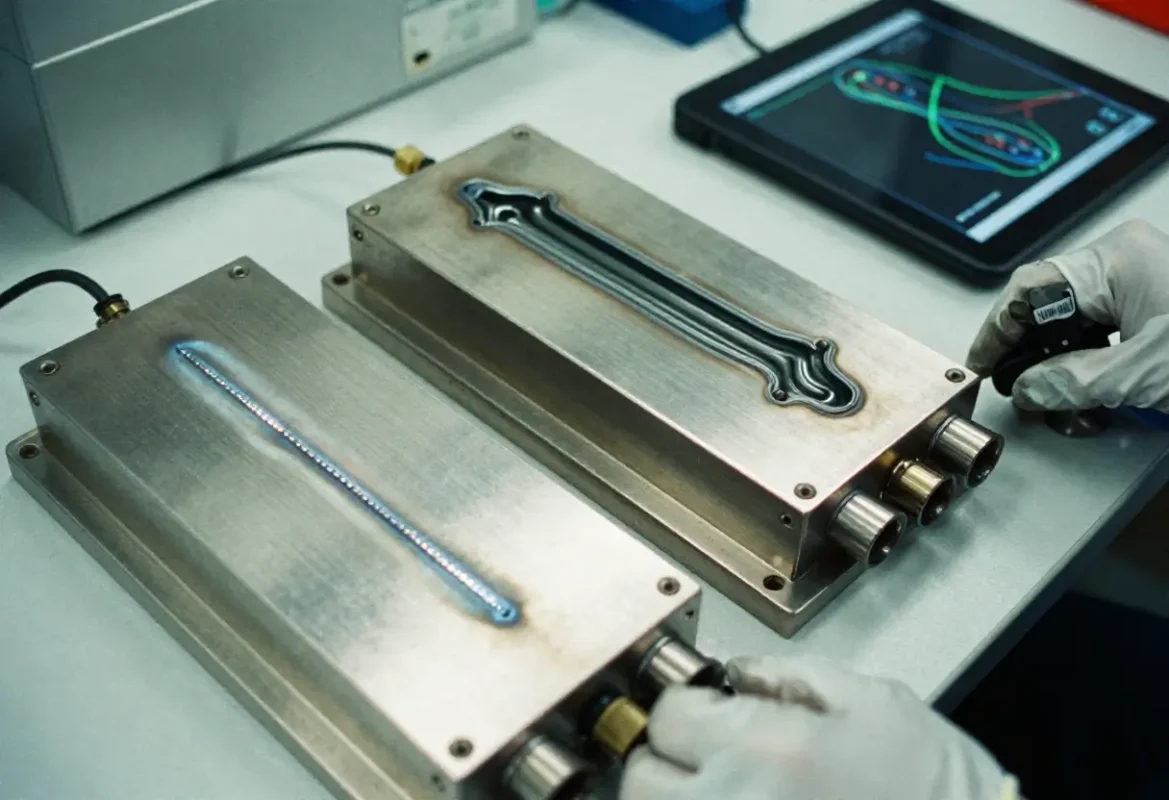

Aluminum
6061: General structural alloy — good machinability, weldability; used for machined brackets and structural parts
7075: High strength — used where high specific strength required; less weldable, often used in forgings and machined parts.
6063 / 6082: Preferred for extrusions with good surface finish and anodizing properties.
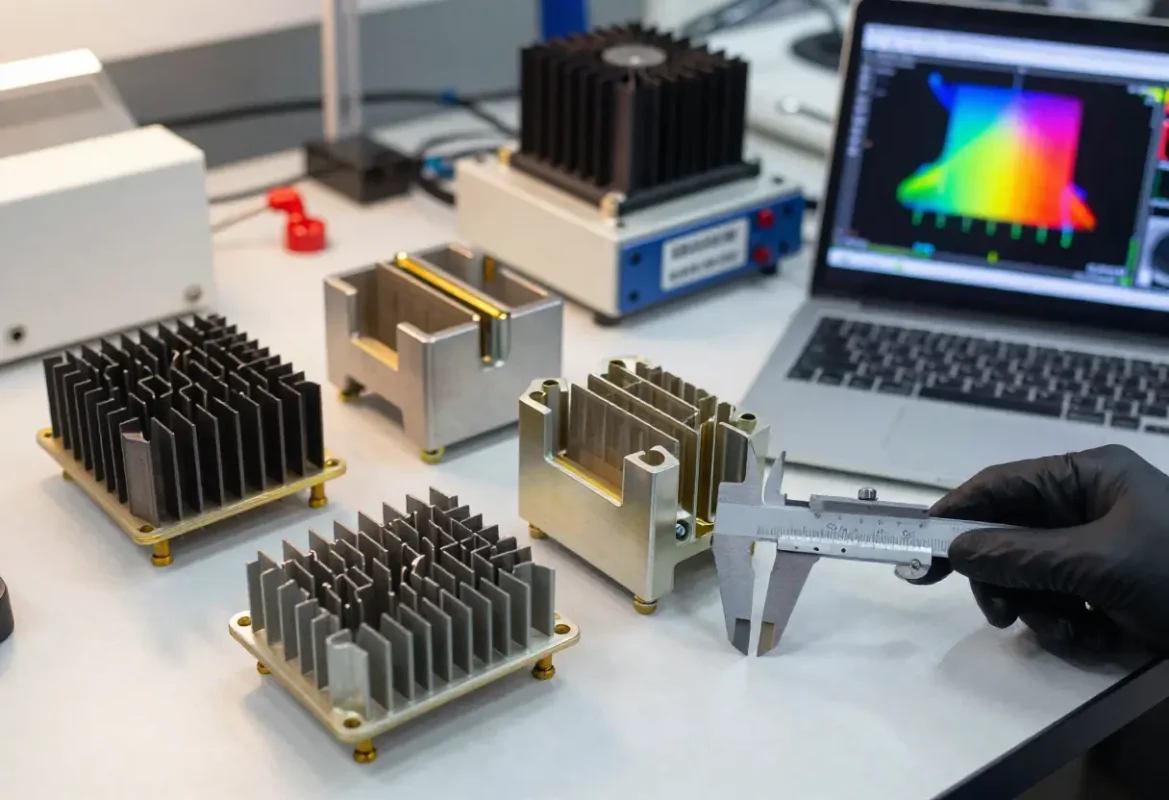

Steels Stainless, Carbon & Alloy
304 / 316: Stainless Common corrosion resistant grades; 316 preferred for chlorides/coastal environments.
420 / 440: Martensitic stainless for hardened, wear‑resistant components (cutlery, shafts).
Carbon & Alloy Steels: AISI 1018/1045 for general machining; 4140, 4340 for higher strength/forging applications.
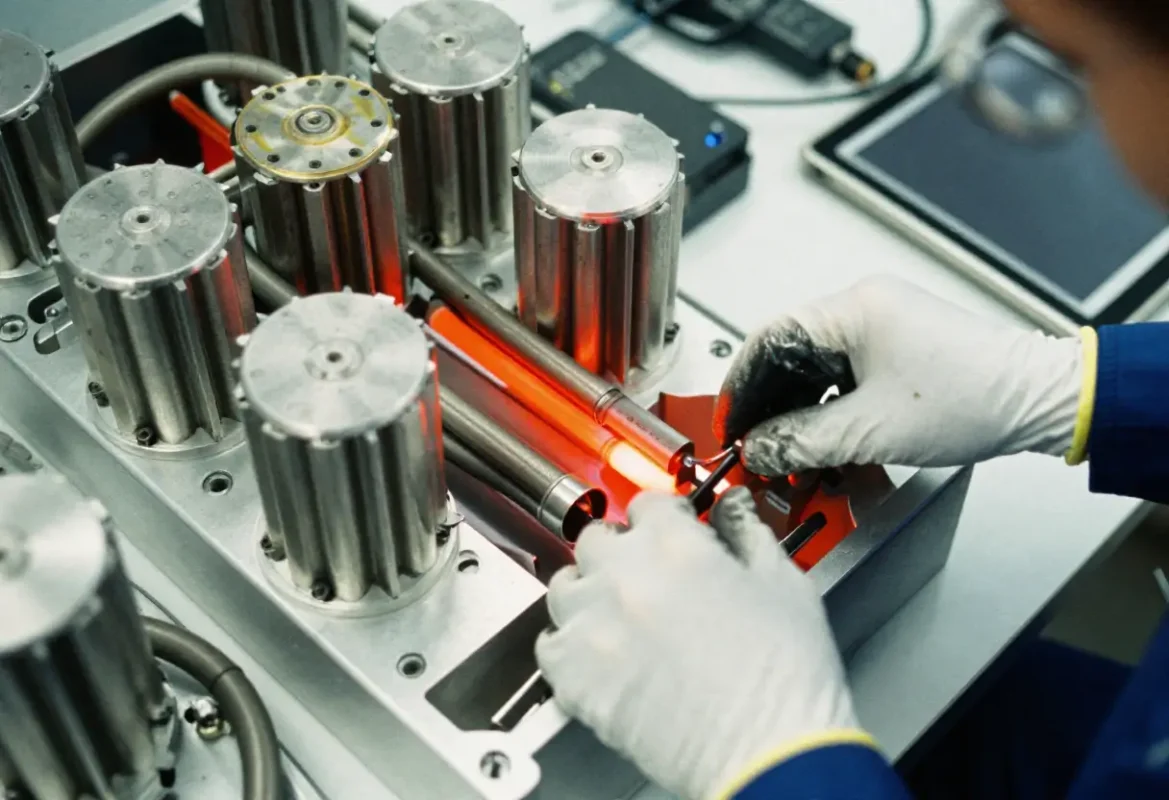
Zinc, Copper/Brass & Titanium
Zinc (Zamak): Zamak 3/5/8 used for high detail die cast parts, excellent plating base and tight cosmetic finishes. Limited temperature and strength vs aluminum.
Copper & Brass: High electrical and thermal conductivity. Brass used for decorative trim and connectors; copper for busbars and thermal interfaces.
Titanium: Exceptional strength‑to‑weight and corrosion resistance — used in aerospace, high‑end motorsport and corrosive environments.
Fabrication & Manufacturing Considerations
Different metals favor different processes. Consider process early when choosing alloy and geometry.

Machining
Aluminum and brass are easy to machine. Hardened steels and titanium require slower feeds and specialized tooling/coatings.

Die Casting & Casting
Aluminum & zinc for high‑volume complex geometry; sand casting for large sections.
Forging & Forming
Forging enhances fatigue life and grain flow; stamping suitable for sheet parts with appropriate springback allowances.
Surface Processing & Coatings
Specify finishing early it affects alloy choice and tolerances. Common finishes and notes:
Anodize (Al)
Clear or color anodize for corrosion protection and consistent appearance; requires compatible alloy and pre‑machining allowances.
Plating
Nickel/chrome on zinc and brass for decorative trims; electroless nickel for corrosion & wear resistance.
Painting / Powder Coat
Economical corrosion protection for steel and aluminum; pre‑treatment required for adhesion and longevity.
Testing, MTRs & Traceability
We provide Material Test Reports (MTRs), hardness, tensile, and chemical assay data as part of qualification. For regulated industries we link MTRs to production lots and include heat‑treat records and non‑destructive testing where required.
| Test | Why & When | Typical Deliverable |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical assay | Validate alloy composition | MTR showing batch composition |
| Tensile / hardness | Mechanical property confirmation | Test report with sample IDs |
| CT / X‑ray | Detect porosity in castings | CT report and porosity map |
| Salt spray / corrosion | Finish and corrosion validation | Salt spray test report |
Material Selection Checklist
- Functional needs: strength, stiffness, fatigue, thermal conductivity
- Manufacturing process: machining, casting, forging, extrusion, stamping
- Environmental exposure: corrosion, temperature, chemicals, UV
- Finishing: anodize, plating, paint, coating compatibility
- Regulatory: RoHS/REACH, FDA, USP, UL, aerospace / automotive standards
- Supply chain: lead time, single‑source risk, MOQ

Representative Projects

Die‑Cast Aluminum Inverter Housing
A356 vacuum die cast housing with post‑machined sealing faces, anodize for corrosion resistance and CT inspection for porosity control.
Forged & Machined Suspension Bracket
Closed‑die forged 4140 bracket, heat treated and machined to tolerances; final plating and fatigue testing for motorsport application.
Need Help Choosing a Metal?
Upload your part CAD, expected loads, operating temperature and environmental conditions. Our materials engineers will recommend candidate alloys, finishing options and required tests typically within 24 business hours.


