Casting & Forging — Sand, Investment, Gravity Casting & Closed / Open‑Die Forging
We offer casting and forging services across processes and alloys to meet structural, thermal and cosmetic requirements. From pattern and coremaking to vacuum casting, forging dies, heat treatment and CNC finishing, we qualify parts with NDT and mechanical testing for safety‑critical and structural applications.
Quick process map
- Investment — best for fine detail, thin walls & high finish
- Sand — flexible for large parts and low tooling cost
- Forging — superior mechanical properties and fatigue life
Casting Processes & When to Use Them
Investment (Lost‑Wax)
Use for high detail, thin walls and excellent surface finish — aerospace, medical and precision pump/turbine components.
Sand Casting
Flexible for large, low‑to‑medium volumes; cost effective for large sections and rapid pattern changes.
Gravity & Low‑Pressure
Gravity for controlled fill with minimal turbulence; low‑pressure for improved density and reduced porosity in structural castings.
Casting best practices
- Perform early solidification simulation to place risers and feeders for directional solidification
- Use vacuum/low‑pressure casting and melt degassing for pressure‑critical or high‑fatigue parts
- Plan post‑cast machining allowances and datum features for sealing faces and critical fits
Forging Processes & Benefits
Forging produces improved grain flow, higher density and superior fatigue and impact properties versus cast parts. We provide closed‑die forging for net‑shape structural parts, open‑die forging for large billets and upset forging for fastener and flange features.
Closed‑Die Forging
Net‑shape parts with fine mechanical properties — used for crank components, connecting rods, large structural brackets.Open‑Die Forging
Large blocks, shafts and flanges where custom section control and directional properties are needed.Upset / Cold Forging
Efficient production of fasteners, bolts and simple geometry parts with excellent material utilization.Design tips for forging
- Design transitions to promote continuous grain flow through critical load paths
- Minimize sudden cross‑section changes, add generous fillets and allow for forging draft
- Coordinate forging with downstream machining to minimize scrap and control critical datums
Alloy Selection & Typical Applications
Steel & Alloy Steels
Forged steels (4140, 4340, stainless martensitic/duplex) for high strength and fatigue critical parts.
Aluminum
A356, A380, ADC12 for castings — A356 for heat‑treatable structural castings; forgings in 6000/7000 series where needed.
Nickel & Titanium
High‑temp and corrosive environments — cast or forged with specialty processes and supplier qualification.
Material considerations
- Design transitions to promote continuous grain flow through critical load paths
- Minimize sudden cross‑section changes, add generous fillets and allow for forging draft
- Coordinate forging with downstream machining to minimize scrap and control critical datums
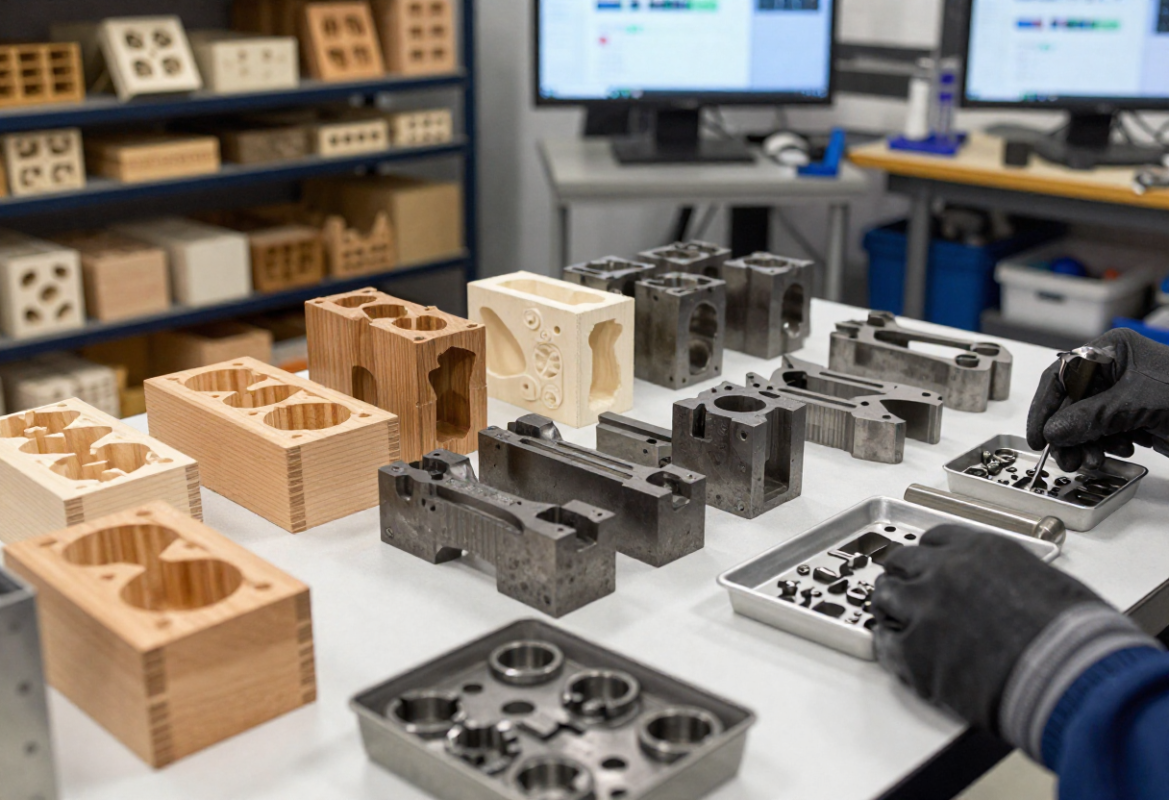
Tooling, Patterns & Dies
We design and build patterns, coreboxes and forging dies with replaceable inserts for wear zones. Tool tryout and maintenance programs include EDM, polishing, die rework and spare inserts to protect uptime.
Patterns & Coreboxes
Wood, epoxy, 3D‑printed and machined patterns for sand and investment processes; coreboxes for internal features and multi‑piece assembly patterns for complex geometry.
Forging Dies
Hardened tool steel, conformal cooling (where applicable), and replaceable inserts to manage wear. Die flow simulation supports load balancing and flash control.

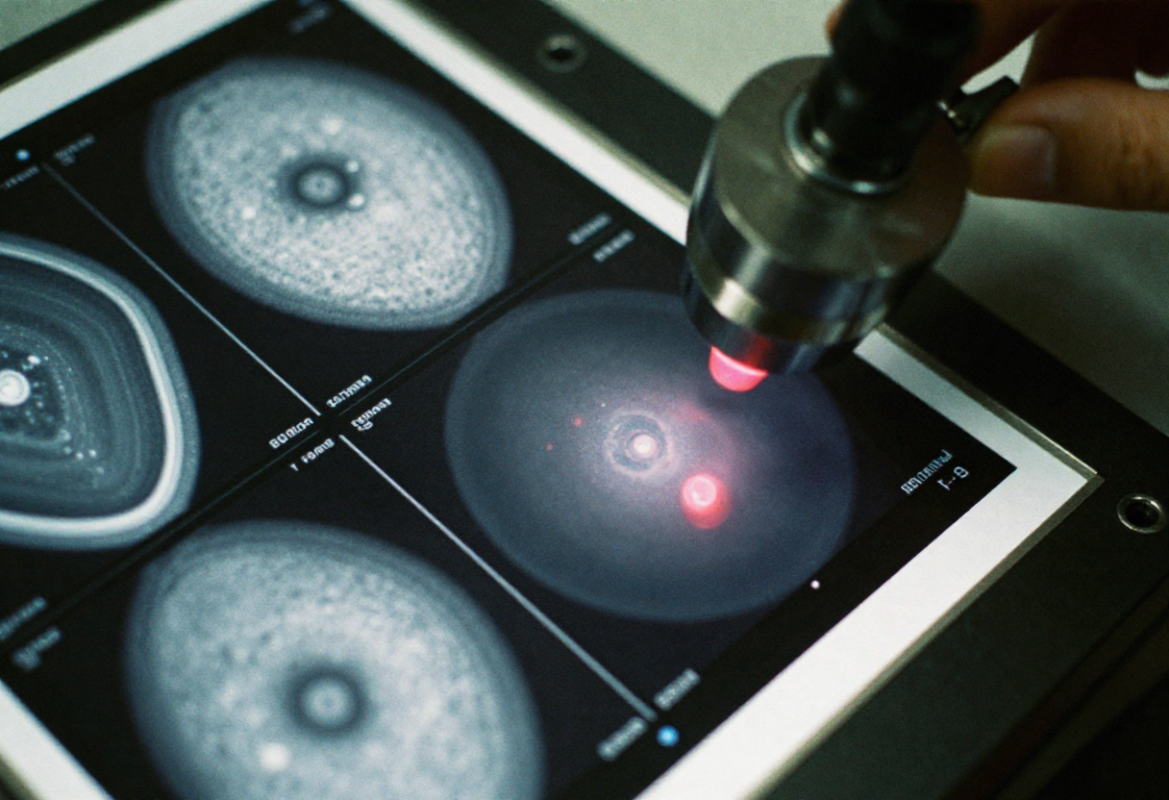
Inspection, NDT & Qualification
Qualification of cast and forged parts uses X‑ray/CT, ultrasonic, dye penetrant, magnetic particle inspection and CMM/optical scanning for critical datums. FAI, PPAP and batch traceability complete production release packages.
NDT Methods
- CT / X‑ray porosity mapping for castings
- Ultrasonic testing for volumetric defects
- Dye penetrant & magnetic particle for surface cracks
Post‑Process Machining & Secondary Operations
After casting or forging we supply CNC finish machining, grinding, welding repairs, surface prep for coating/plating, leak testing for housings and final assembly. Fixtures and datum strategies ensure critical sealing and bearing surfaces meet requirements.
Surface Treatment & Finishes
Finish options include shot blasting, polishing, machining, plating, anodize (for aluminum after machining), powder/wet paint, and protective conversion coatings. Specify finish zones and post‑finish critical datums early.
Lead Times & Typical Schedules
| Item | Typical Lead Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Investment pattern & first articles | 4–10 weeks | Depends on complexity and shell cycles |
| Sand casting pattern & tryout | 2–6 weeks | Rapid iteration possible |
| Forging die & trial | 8–20+ weeks | Die complexity and heat treat add time |
| CT/X‑ray qualification | 1–3 weeks | Depends on part count and resolution |
Representative Projects
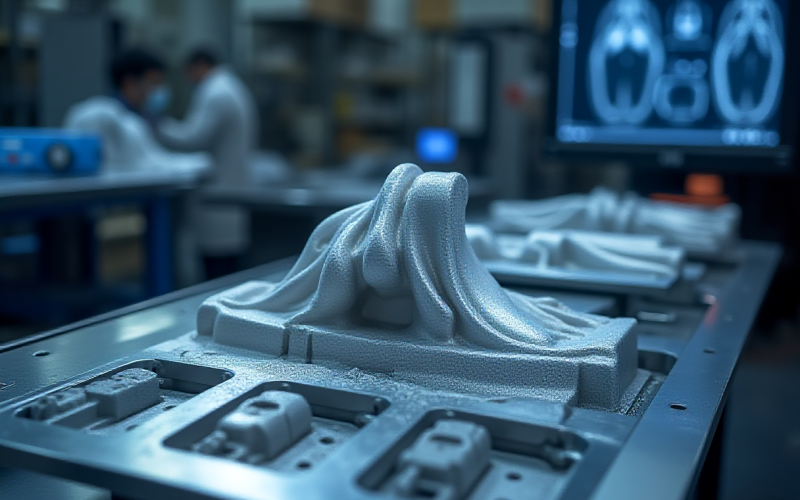

Vacuum Investment Turbine Bracket
Investment casting of complex thin‑wall bracket followed by CNC finishing and CT inspection for aerospace structural application.
Closed‑Die Forged Steering Knuckle
Closed‑die forged steel knuckle with precision machining of bearing journals, heat treat (quench & temper) and ultrasonic inspection for automotive program.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I choose between sand and investment casting?
Choose investment for fine detail, thin walls and superior surface finish; choose sand for large parts, flexible tooling and lower upfront cost. We assess geometry, tolerances and volumes to recommend the best process.
Can forged parts be welded for assemblies?
Yes — forged components are often welded for assemblies. Welding procedures, pre/post heat treatment and filler metal selection are validated to maintain mechanical integrity.
What inspections are typical for cast structural parts?
CT/X‑ray for internal porosity, ultrasonic for volumetric defects, dye penetrant for surface flaws, and mechanical testing (tensile, hardness) per spec. Inspection scope depends on criticality and standards.
Start Your Casting or Forging Project
Upload your CAD, material and functional requirements. We’ll propose a process (casting vs forging), tooling concept, porosity mitigation plan and estimated lead times — typically within 24 business hours.


