Rubber & Silicone LSR, VMQ, EPDM, NBR, FKM & TPE Guidance
Overview of common elastomer families, material properties, molding processes (LSR injection, compression, transfer), tooling considerations, post‑cure and testing. Useful for selecting sealing, gasketing, soft‑touch and medical elastomer solutions from prototype through volume production.
Material families: LSR (liquid silicone), VMQ (high temp silicone), EPDM, NBR, FKM (Viton), TPE/TPU
Molding: LSR injection, compression, transfer, overmolding and multi‑shot
Tooling & post‑process: cavity polish, venting, post‑cure, trim automation and cleanroom options
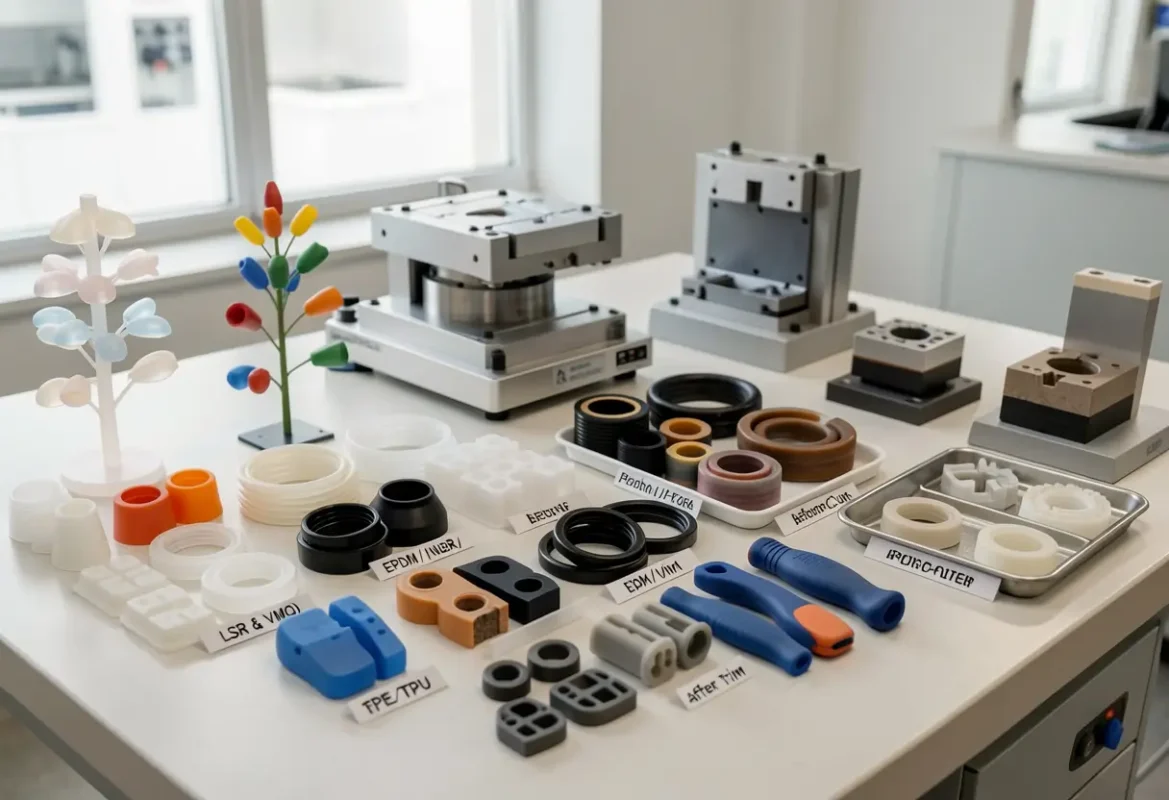

Elastomer Families & Typical Applications

Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)

VMQ / HCR Silicone

EPDM
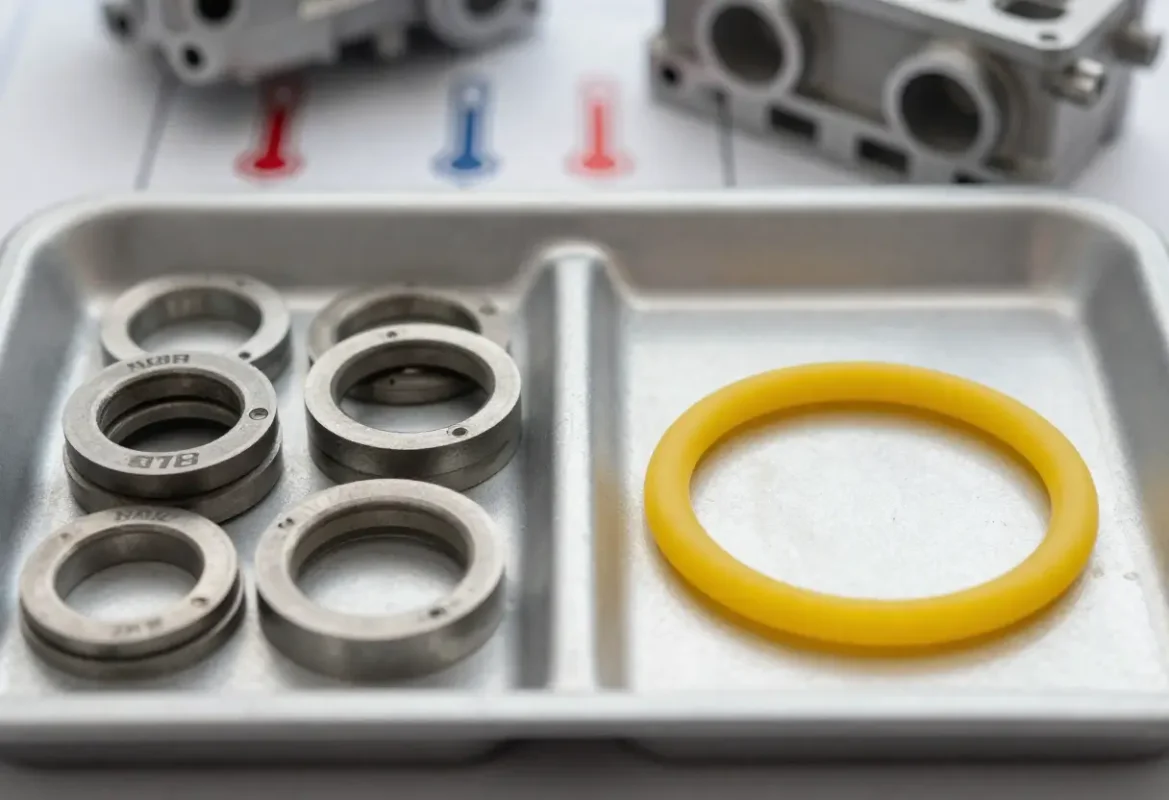

NBR (Nitrile)
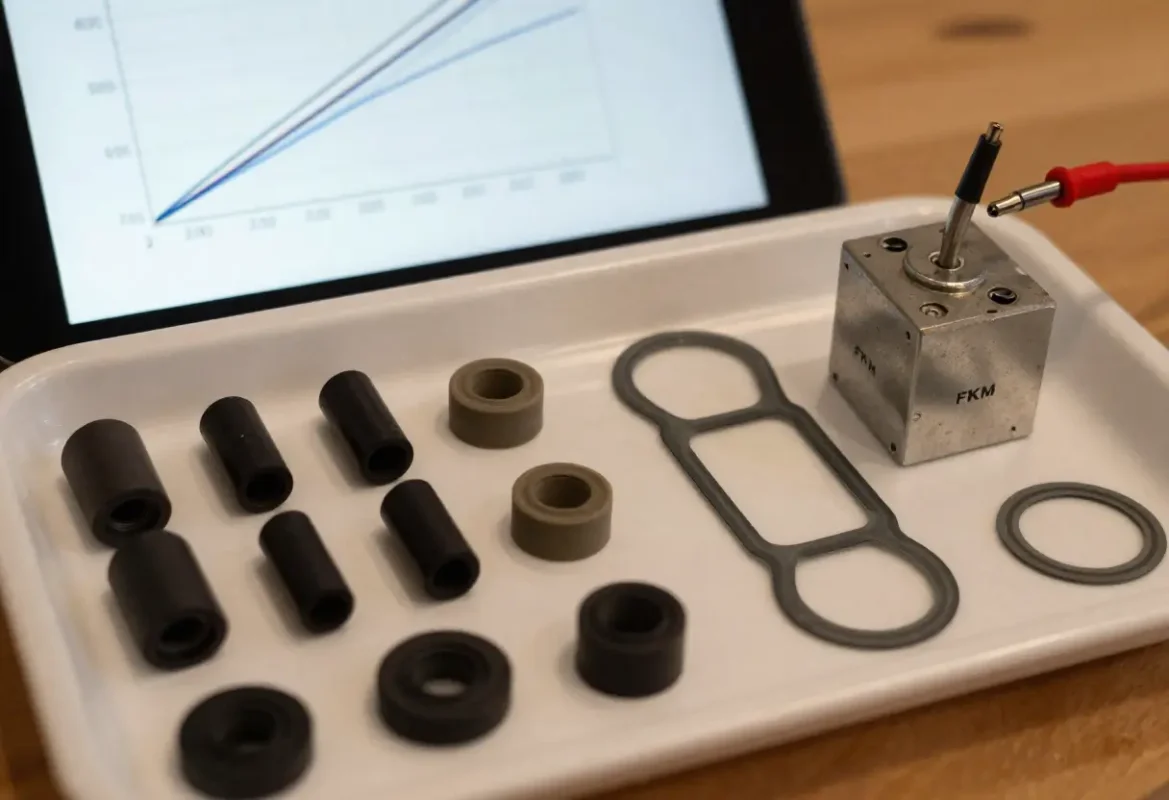

FKM (Viton)
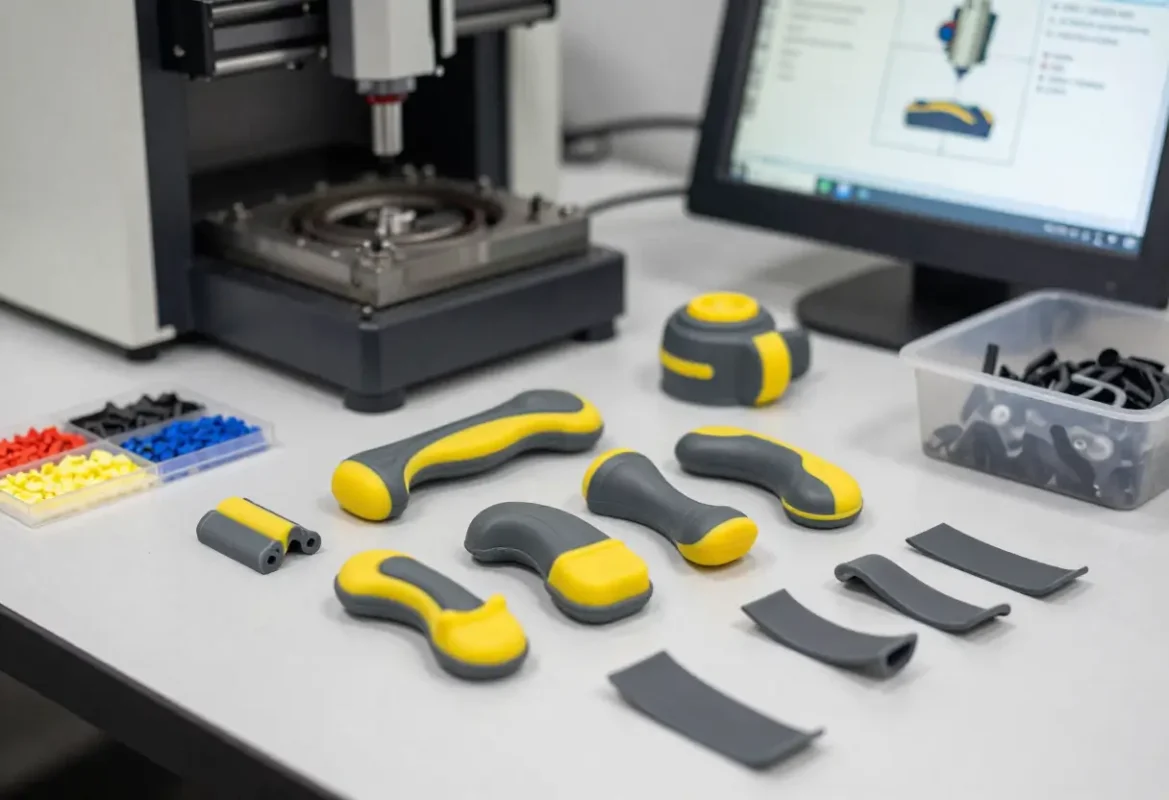

TPE / TPU
Key Properties & Durometer Guidance
Durometer
Common ranges Shore A 10–90; lower values are softer (better sealing/comfort); higher values give load‑bearing capability.
Compression set
Lower is better for sealing specify limits after thermal aging tests.
Tear & tensile
Important for dynamic seals and stretch fits.
Compression set
Silicone: -60°C to +200°C; EPDM up to ~150°C; FKM up to 200+°C depending on grade
Molding Processes LSR, Compression, Transfer & Overmolding
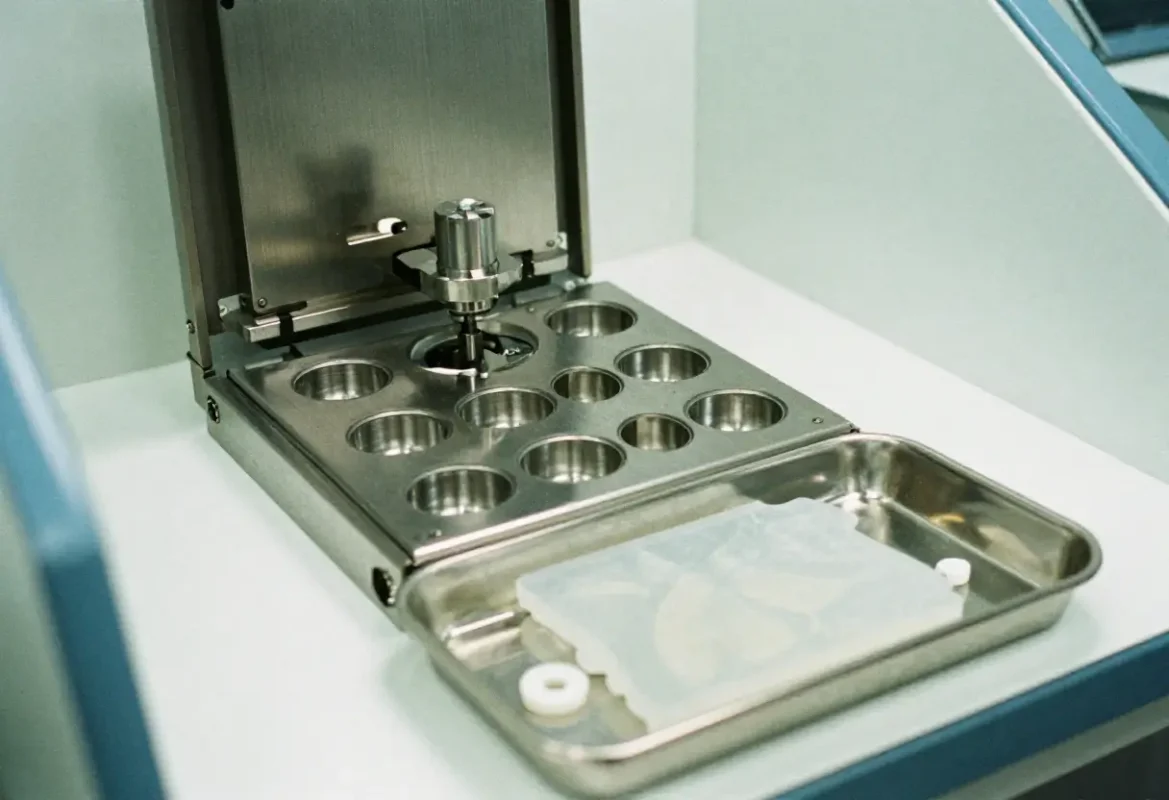
LSR Injection Molding
Metered 2‑component injection into stainless cavities. Benefits: high repeatability, low contamination, automated degating and high cosmetic quality. Often integrated with automated pick‑and‑place and in‑line post‑cure ovens.

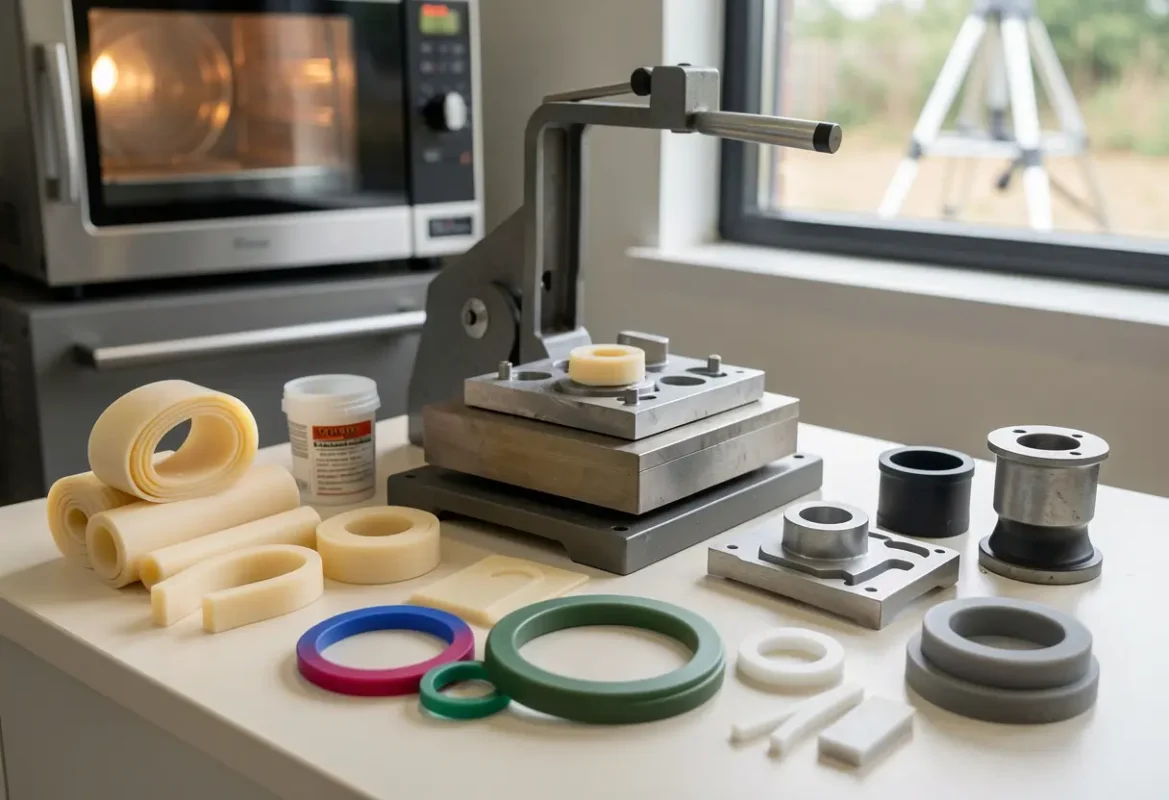
Compression & Transfer Molding
Compression uses premeasured charge pressed between heated halves good for large or thick parts. Transfer injects preheated compound through sprues to cavities — offers better flash control and repeatability versus compression.
Tooling & Design Considerations
Tooling for elastomers differs from rigid plastics: cavity materials (stainless / hardened steels), mirror polish for cosmetic silicones, venting to release volatiles, heater zones and controlled thermocouples. For LSR, use stainless cavities with controlled venting and dedicated post‑cure ovens.
- Polish level & texture mapped per cosmetic zones
- Micro‑vents & gas traps for proper fill and reduced pinholes
- Insert fixturing and retention features to avoid movement during molding
- Provision for degassing and shot traceability (LSR metering)
Post‑Cure, Trim & Automation
Many elastomers require post‑cure to stabilize properties and reduce volatile extractables. LSR often needs a short post‑cure; HCR/sulfur cured rubbers require longer thermal cycles. Automated trimming (waterjet, laser, mechanical punch) and vision inspection improve throughput and consistency.
- Molded part → degating / flash removal (automated where feasible)
- Post‑cure per compound (oven or IR systems)
- Automated trim & dimensional/vision inspection
- Package & lot traceability (critical for medical parts)
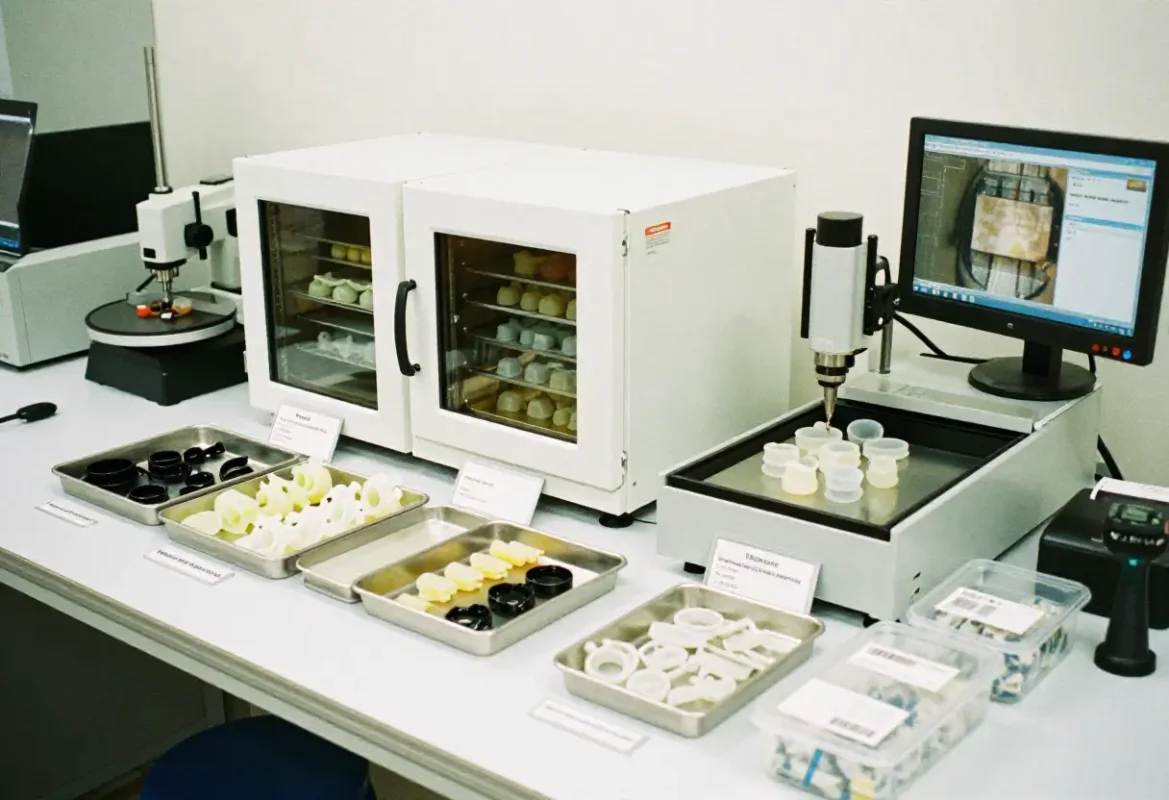

Testing & Qualification

Mechanical & environmental tests
- Durometer (Shore A), tensile & tear
- Compression set after aging
- Thermal cycling, UV and ozone exposure

Regulatory & lab tests
- ISO 10993, USP extracts for medical/implantable parts
- Food contact approvals, FDA guidance
- Material certificates and lot traceability for each production run
Design for Elastomers Practical Guidance
- Keep minimum wall thickness suitable for durometer (softer materials need thicker sections to avoid tearing)
- Use generous radii and fillets; sharp corners increase tear risk
- Design sacrificial flash areas for automated trimming
- For seals, define mating surface finish and hardness to ensure leakage performance
- Consider tolerances: elastomers are more variable — specify functional limits rather than tight dimensional tolerances
| Feature | Recommendation | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Min wall | ≥ 1.0 mm (depends on durometer) | Very soft compounds require more thickness |
| Draft | 0.5°–2° | Increase for textured surfaces |
| Flash allowance | Provide accessible flash lands | Automated trim benefits from consistent flash geometry |
Material Sourcing & Lead Times

Representative Projects

Medical Valve Seal (LSR)
Increases modulus and dimensional stability; increases density and tool wear.
Automotive Boot (EPDM Compression)
Compression molded EPDM boot with designed flash lands for automated trimming and validated long‑term compression set under heat and oil exposure.


