Materials Overview Metals, Plastics, Elastomers & Finishes
A consolidated reference to choose materials, understand tradeoffs, verify finish compatibility and plan testing & compliance. Use this page during early DFM to shortlist candidate materials for mechanical, thermal, chemical and regulatory requirements.
- Guidance for alloy/plastic/elastomer selection based on performance and manufacturability
- Surface finishing compatibility and performance coatings
- Testing, certification and supply chain considerations for prototype → production

Metals Selection & Typical Use Cases
Metals provide structural strength, thermal conductivity, wear resistance and often form the primary choice for housings, heat sinks, fasteners and load‑bearing parts. Selection depends on mechanical, thermal and corrosion needs as well as manufacturability (machining, casting, stamping, forging).
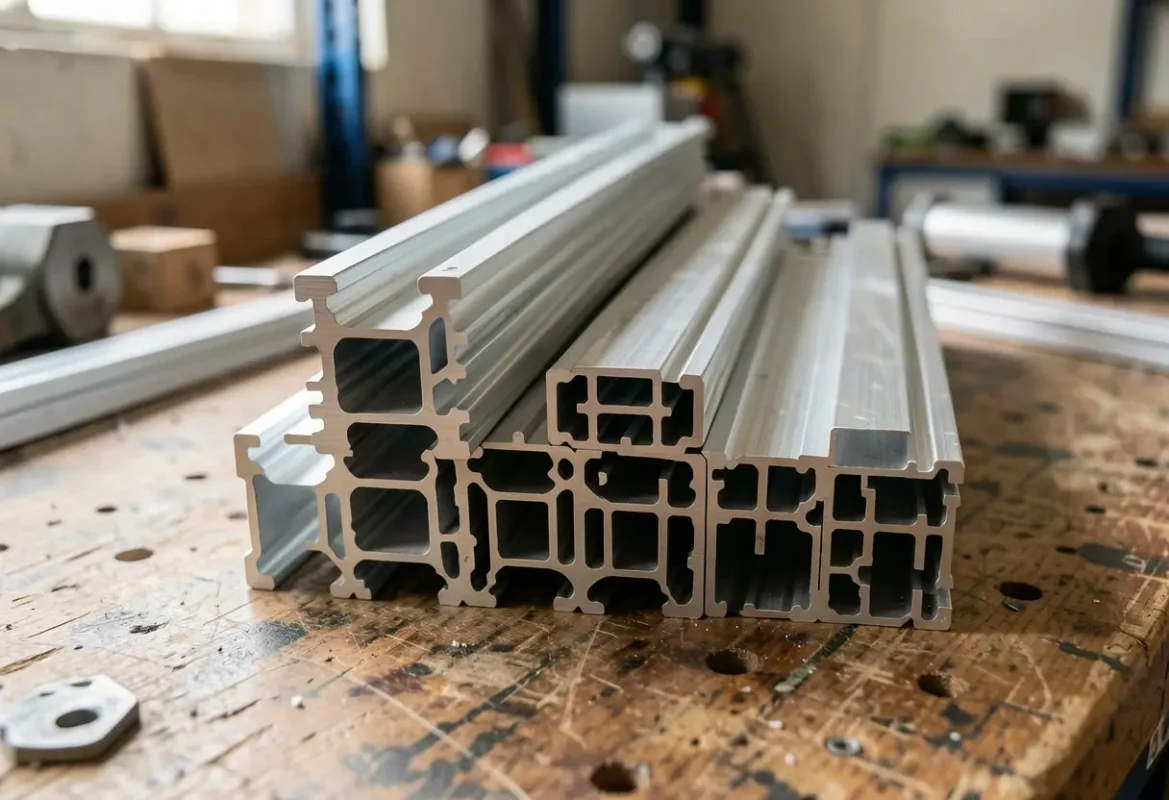

Aluminum
6061 & 7075 for machined structural parts; 6063 for extrusions; ADC12/A380/A356 for die casting. Excellent strength‑to‑weight and thermal conductivity; anodize compatible.
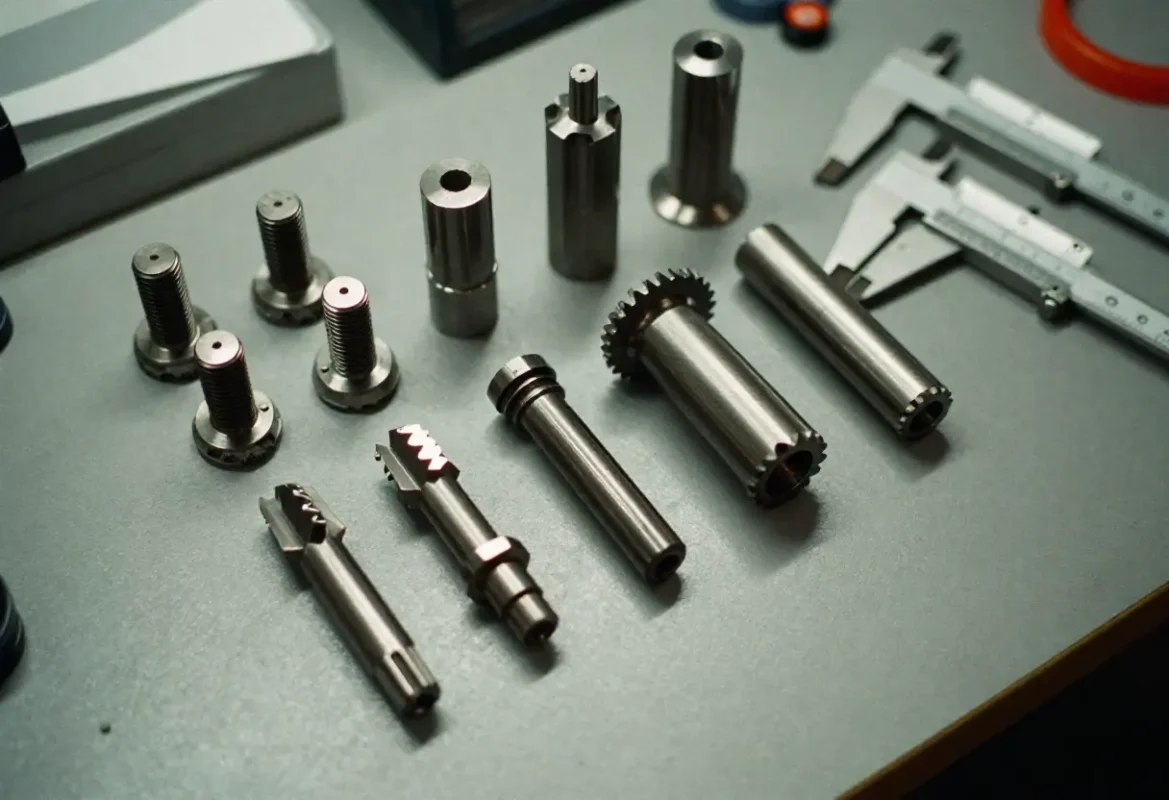

Stainless Steel
304/316 for corrosion resistance; 420 for hardened components. Used where corrosion, cleanliness or high temperature required.
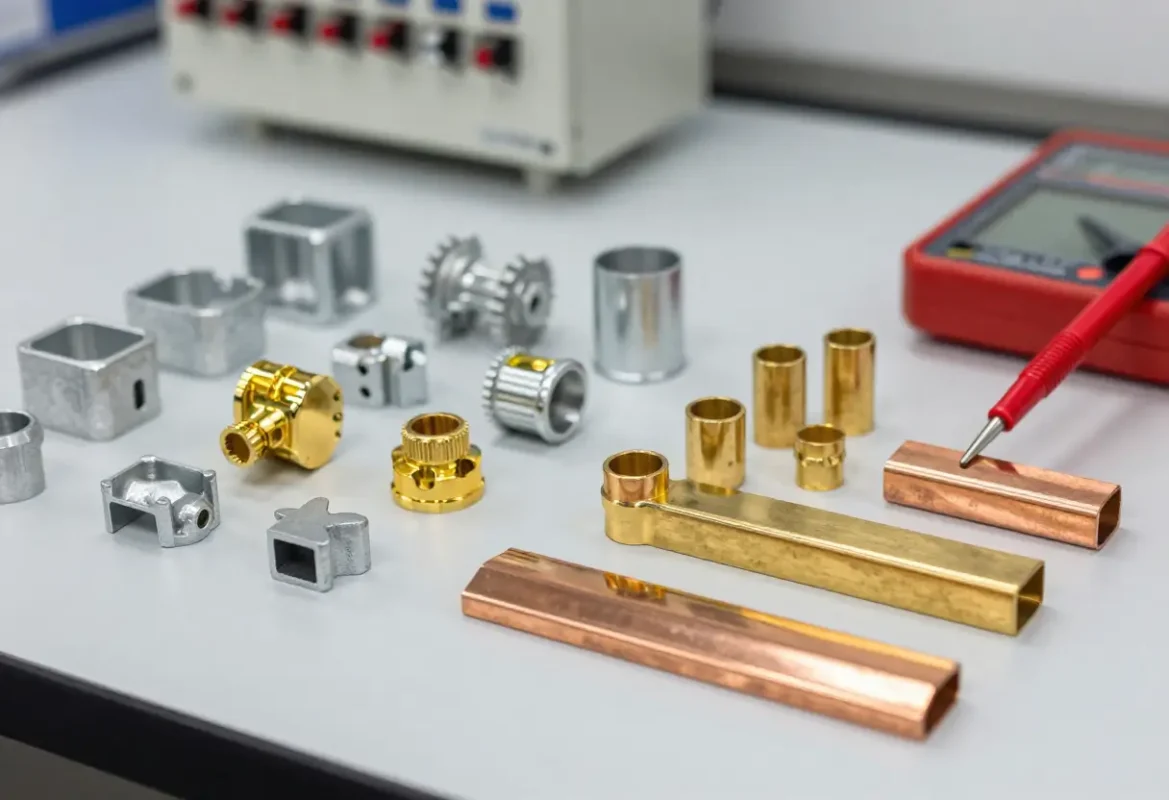

Zinc & Brass
Zamak alloys for high‑detail die cast parts and excellent plating; brass/copper for electrical conductivity and decorative trim.
Plastics Engineering Resins & Applications
High‑Performance
PEEK, PEI (ULTEM): high temp, chemical resistance, used for power electronics insulators and demanding mechanical parts.
Engineering Thermoplastics
PA66, POM, PBT, PP — good mechanical strength and wear resistance for structural components and gears.
Cosmetic / Structural Blends
ABS, PC, PC/ABS blends for housings with good surface finish and impact resistance; PC for transparent/optical parts.
Rubber & Silicone Properties & Typical Uses
Elastomers provide sealing, vibration isolation and soft‑touch surfaces. Selection depends on temperature range, chemical exposure, compression set and regulatory needs (medical/food contact).
Silicones / LSR
Excellent temperature range, biocompatibility, low extractables for medical/food contact; LSR used for high‑repeatability injection molding.
EPDM / NBR / FKM
EPDM for weather/steam; NBR for oil/grease resistance; FKM (Viton) for high chemical/temperature resistance.
TPE / TPU
Thermoplastic elastomers for overmolding, recyclability and simplified processing vs thermoset rubbers.
Surface Finishing — Functional & Cosmetic Options
Surface finishing affects corrosion resistance, appearance, wear and friction. Choose finishes that are compatible with base material and downstream assembly or regulatory needs.
Anodizing
Aluminum anodize (clear, hard, color) for corrosion protection and decorative finishes; hard anodize for wear resistance.
Plating & Coatings
Nickel, chrome, electroless nickel for aesthetic and corrosion resistance — ensure substrate compatibility (zinc, brass, aluminum). Powder coat and wet paint for color and texture.
Functional Coatings
Thermal interface coatings, anti‑fingerprint, anti‑UV and corrosion inhibiting coatings for performance requirements.
Finish Compatibility Matrix (excerpt)
| Material | Typical Finishes | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Anodize, powder coat, wet paint | Anodize best for corrosion & aesthetics; use conversion coating prior to paint |
| Steel (galv) | Powder coat, wet paint, e‑coating | Pre‑treatment required for adhesion & corrosion |
| Zinc (Zamak) | Nickel/chrome plating, PVD | Excellent plating base for decorative trims |
| Plastics | Painting, pad/screen print, soft‑touch coatings | Surface prep (primer) needed for adhesion |
Performance & Specialty Coatings
Special finishes add functionality beyond aesthetics: corrosion resistance, thermal control, EMI shielding, anti‑slip and anti‑microbial coatings. These are often specified at system level and may require validation testing.
- Corrosion resistant: conversion coatings, nickel/EN plating, passivation for stainless
- Thermal coatings: high emissivity paints, thermal interface compounds
- EMI/RFI: conductive coatings, shielding gaskets, plated housings
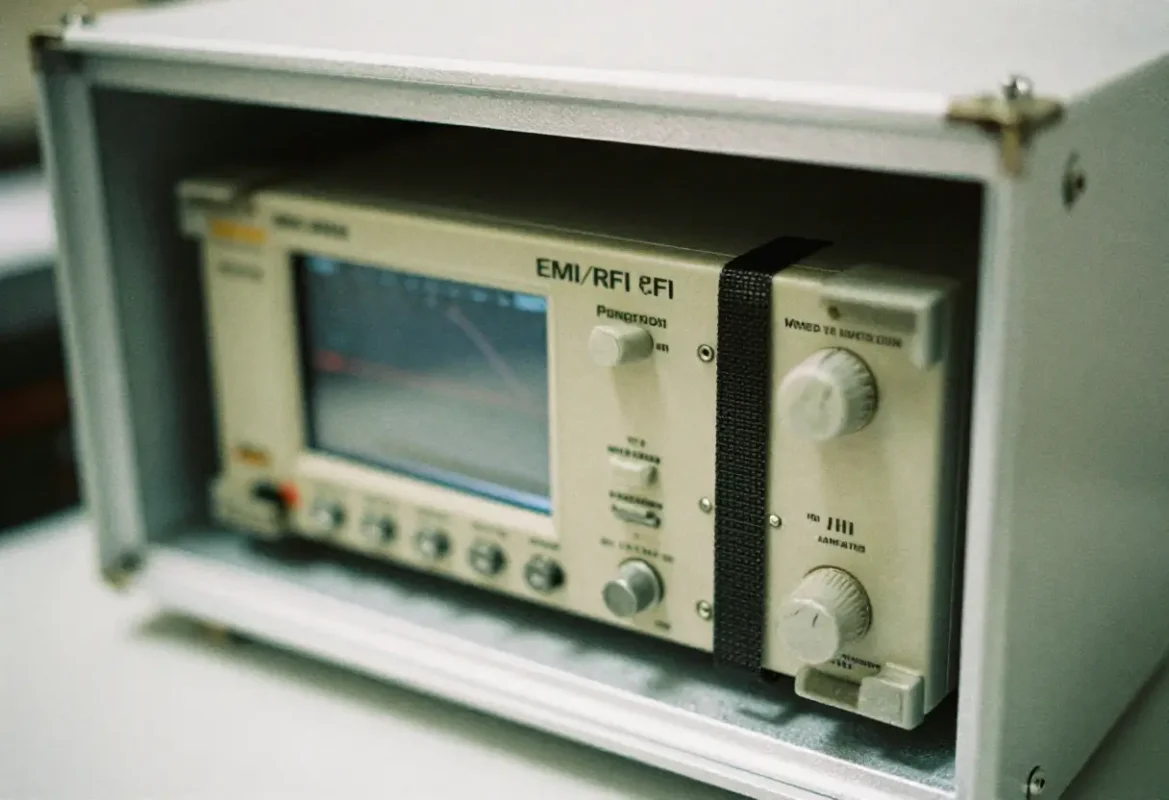

Testing, Validation & Regulatory Compliance
Material certification and testing are essential for regulated industries. Typical deliverables include material MTRs, tensile/hardness assays, flammability (UL), biocompatibility (ISO 10993), extractables/ leachables, RoHS/REACH declarations, and FAI/PPAP packages for production release.
Common tests
Tensile, elongation, modulus and hardness Thermal (Tg, HDT), DSC, TGA for plastics Durometer, compression set, tear and tensile for elastomers Salt spray, corrosion and environmental aging for finishes

Compliance & certifications
RoHS / REACH / Conflict Minerals screening UL / IEC / EN standards for electrical & flammability FDA / USP / ISO 10993 for medical materials Material Test Reports (MTR) and certificate of conformity (CoC)
Sourcing, Lead Times & Supply Chain Considerations
Material availability, long lead times for specialty alloys or filled resins, and minimum order quantities affect program economics. Early engagement with procurement helps mitigate risk: approve multiple qualified suppliers, evaluate substitute materials, and consider inventory strategies (VMI, consignment) for critical items.
Procurement tips
- Identify long‑lead or single‑source materials in concept phase
- Qualify alternates for obsolescence mitigation
- Plan packaging and humidity control for sensitive materials

Sustainability & End‑of‑Life
Consider recyclability and embodied carbon during material selection. Aluminum and steel are highly recyclable; many thermoplastics are recyclable but may need separation from mixed materials and coatings. Evaluate coating recyclability and ease of disassembly for repair/recycling.
Practical steps
- Prefer single‑material design where possible to simplify recycling
- Choose finishes that do not prevent metal recycling (avoid heavy mixed coatings where possible)
- Document material composition for downstream recycling & regulatory reporting

Quick Reference Material Selection Matrix (excerpt)
| Requirement | Top Material Choices | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Lightweight structural | Aluminum 6061/7075, Titanium | Aluminum for cost/thermal; titanium for extreme environments |
| High temp / chemical | PEEK, PEEK‑filled, FKM | Use for sustained high temperatures & harsh chemicals |
| Seals / gaskets | LSR, Silicone, EPDM, FKM | Select by temp & chemical compatibility |
| Decorative plated parts | Zamak, Brass, Stainless | Zinc/brass excellent for plating and detail |
| EMI shielding | Die cast Al (plated), conductive coatings | Design for grounding and gasket integration |


